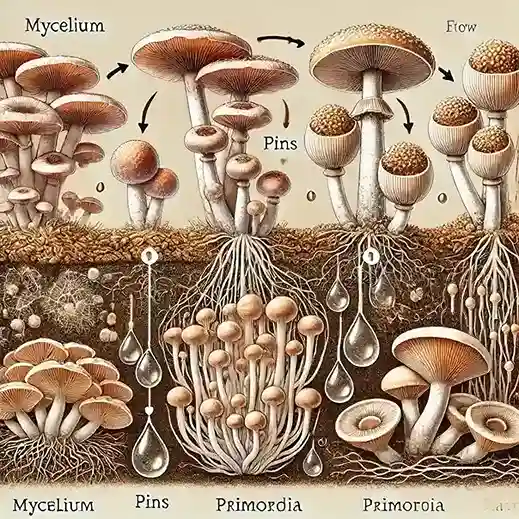
Mushroom fruiting begins with the formation of primordia, which develop into mature mushrooms. This process requires specific environmental conditions.
Mushrooms are fascinating fungi that undergo a unique fruiting process. Initially, mycelium, the vegetative part of the fungus, spreads through the substrate. Under optimal conditions such as appropriate humidity, temperature, and light, the mycelium forms tiny, pin-like structures called primordia.
These primordia grow and mature into the fruiting bodies we recognize as mushrooms. Proper air circulation and moisture levels are crucial during this stage. The entire cycle from mycelium to mature mushroom can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. Understanding these steps helps in successful mushroom cultivation and harvesting.
Introduction To Mushroom Fruiting
The mushroom fruiting process is crucial in mushroom cultivation. This process transforms mycelium into actual mushrooms. It is fascinating and essential for mushroom growers.
Importance Of Fruiting
The fruiting stage is the final step in mushroom growth. During this stage, mushrooms develop and mature. Successful fruiting ensures a good mushroom yield. It impacts both quality and quantity. Proper fruiting conditions are necessary for healthy mushrooms.
Common Mushroom Varieties
| Mushroom Variety | Common Name | Optimal Fruiting Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Agaricus bisporus | Button Mushroom | High humidity, moderate temperature |
| Pleurotus ostreatus | Oyster Mushroom | Cool temperature, high humidity |
| Lentinula edodes | Shiitake Mushroom | Warm temperature, moderate humidity |
-
- Button mushrooms are popular and easy to grow.
- Oyster mushrooms are known for their rapid growth.
- Shiitake mushrooms have a unique flavor and texture.

Credit: www.midwestgrowkits.com
Choosing The Right Substrate
Choosing the right substrate is crucial for a successful mushroom fruiting process. The substrate provides the necessary nutrients for mushroom growth.
Different mushrooms need different substrates. Picking the correct one ensures healthy and abundant mushrooms.
Types Of Substrates
There are various types of substrates used in mushroom cultivation. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks. Here are some popular choices:
-
- Straw: Commonly used for oyster mushrooms.
- Sawdust: Ideal for shiitake and lion’s mane mushrooms.
- Compost: Best for button mushrooms.
- Coffee Grounds: Suitable for growing oyster mushrooms.
Preparing The Substrate
Proper preparation of the substrate is essential. It ensures the mushrooms have the right environment to grow. Follow these steps for successful preparation:
-
- Hydrate: Soak the substrate in water. Ensure it is fully moist.
- Pasteurize: Heat the substrate to kill unwanted organisms. This can be done by boiling or steaming.
- Cool: Let the substrate cool down to room temperature.
- Inoculate: Add mushroom spores or spawn to the substrate. Mix well to distribute evenly.
By following these steps, you create an optimal environment for mushroom growth. Ensure cleanliness throughout the process to avoid contamination.
| Substrate | Suitable for |
|---|---|
| Straw | Oyster Mushrooms |
| Sawdust | Shiitake, Lion’s Mane |
| Compost | Button Mushrooms |
| Coffee Grounds | Oyster Mushrooms |
Choosing and preparing the right substrate is key to growing mushrooms successfully. Pay attention to the type and preparation steps to ensure healthy growth.
Inoculating The Substrate
Inoculating the substrate is a critical step in the mushroom fruiting process. This step involves introducing mushroom spores or mycelium into the substrate.
The goal is to create an environment where mushrooms can grow and thrive. Proper inoculation ensures healthy and abundant mushroom growth.
Spore Selection
Selecting the right spores is crucial for successful mushroom cultivation. Spores are the tiny reproductive units of mushrooms.
They determine the type and quality of the mushrooms you will grow. It’s essential to choose high-quality spores from a reputable source.
-
- Choose spores based on the mushroom variety you wish to grow.
- Ensure spores are free from contaminants.
- Opt for spores that are fresh and viable.
Inoculation Techniques
Various techniques exist for inoculating the substrate. Each method has its own set of advantages. The choice of technique depends on the type of mushroom and the growing conditions.
| Technique | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Spore Syringe | Inject spores into the substrate using a syringe. | Beginner growers |
| Grain Spawn | Mix colonized grains with the substrate. | Commercial growers |
| Agar Culture | Transfer mycelium from agar plates to substrate. | Advanced growers |
-
- Spore Syringe: Simple and effective for beginners.
- Grain Spawn: Ideal for large-scale cultivation.
- Agar Culture: Best for precise mycelium growth.
Proper inoculation techniques ensure the substrate is fully colonized. This leads to robust and healthy mushroom growth.

Credit: grocycle.com
Incubation Period
The Incubation Period is a crucial stage in the mushroom fruiting process. During this phase, the mycelium grows and establishes itself. This period sets the foundation for healthy mushroom development.
Ideal Conditions
Creating the ideal conditions for mycelium growth is essential. The right temperature, humidity, and light levels must be maintained.
-
- Temperature: Keep the environment between 70-75°F (21-24°C).
- Humidity: Maintain humidity levels at 90-95%.
- Light: Low light conditions work best during incubation.
Monitoring Growth
Regularly monitoring growth ensures the mycelium is healthy and thriving. Check for signs of contamination and ensure consistent conditions.
-
- Inspect the mycelium daily.
- Look for any discoloration or unusual growth.
- Adjust temperature and humidity as needed.
| Condition | Optimal Range |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 70-75°F (21-24°C) |
| Humidity | 90-95% |
| Light | Low light |
Initiating Fruiting
The mushroom fruiting process is a fascinating journey. It all begins with initiating fruiting. This stage requires specific conditions to trigger mushroom growth. Let’s explore these conditions.
Environmental Triggers
Mushrooms need the right environmental triggers to start fruiting. Light, fresh air, and humidity are crucial. A sudden change in these can signal the mushrooms to fruit.
-
- Light: Indirect light works best for most mushrooms.
- Fresh Air: Mushrooms need fresh air to grow strong.
- Humidity: High humidity keeps the mushrooms hydrated.
Temperature And Humidity
Temperature and humidity are vital for mushroom fruiting. Different mushrooms prefer different temperatures.
| Mushroom Type | Optimal Temperature | Humidity Level |
|---|---|---|
| Oyster Mushrooms | 55-65°F (13-18°C) | 80-90% |
| Shiitake Mushrooms | 60-70°F (15-21°C) | 75-85% |
| Button Mushrooms | 50-60°F (10-15°C) | 85-95% |
Maintaining the right balance is key. Too much or too little can hinder growth. Use a humidifier to control humidity. Adjust the temperature with heaters or coolers.
Maintaining Fruiting Conditions
The mushroom fruiting process requires careful maintenance of specific conditions. Maintaining these conditions ensures healthy and abundant mushroom growth. This section covers the key elements to focus on: light requirements and air circulation.
Light Requirements
Mushrooms need some light to grow well. Unlike plants, mushrooms don’t use light to make food. Instead, light helps them know which way to grow. They need 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness each day. A simple lamp or indirect sunlight works well. Avoid direct sunlight, as it can dry out the mushrooms.
Air Circulation
Good air circulation is crucial for mushrooms. They need fresh air to grow properly. Stale air can cause problems like mold. Use a small fan to keep the air moving. Make sure the area is well-ventilated. This helps to remove excess carbon dioxide. Also, check the humidity levels. Mushrooms thrive in a humid environment.
Harvesting Mushrooms
Harvesting mushrooms is a crucial part of the mushroom fruiting process. It ensures you pick them at their peak freshness and flavor. Knowing the right time and technique is essential for a bountiful harvest.
Signs Of Readiness
Recognizing the signs of readiness helps in harvesting mushrooms at their best. Look for these indicators:
-
- Cap Size: The cap is fully opened but not too wide.
- Color: The mushroom cap has a consistent color.
- Gills: The gills are visible but not too dark.
- Stem: The stem is firm and not too long.
Harvesting Techniques
Using the right harvesting techniques ensures you get the best mushrooms. Here are some methods:
-
- Twist and Pull: Gently twist the mushroom stem and pull it out.
- Cutting: Use a sharp knife to cut the mushroom at the base.
- Clean Hands: Always use clean hands or gloves to avoid contamination.
Using these techniques will help you harvest mushrooms efficiently. Happy harvesting!

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Post-harvest Care
Post-harvest care is crucial for maintaining the quality of mushrooms. Proper handling ensures mushrooms stay fresh and tasty. This section will cover essential storage and preservation methods.
Storage Methods
Storing mushrooms correctly helps maintain their freshness and flavor. Follow these tips:
-
- Refrigeration: Store mushrooms in a paper bag in the fridge. This method keeps them fresh for up to a week.
- Avoid Plastic Bags: Plastic traps moisture and promotes spoilage. Always use paper bags.
- Humidity Control: Ensure the fridge has low humidity. High humidity causes mushrooms to mold.
Here’s a quick comparison of different storage methods:
| Storage Method | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Paper Bag in Fridge | Up to 1 week | Best for freshness |
| Plastic Bag in Fridge | 2-3 days | Not recommended |
| Room Temperature | 1-2 days | Use only for immediate consumption |
Preservation Techniques
Preservation techniques extend the shelf life of mushrooms. Here are some effective methods:
-
- Drying: Dehydrating mushrooms is a great way to store them long-term. Use a food dehydrator or oven. Once dried, store in an airtight container.
- Freezing: Freeze mushrooms to keep them for months. First, clean and slice them. Then, blanch in boiling water for 2 minutes. Finally, spread on a tray to freeze before transferring to a bag.
- Pickling: Pickling mushrooms adds flavor and extends their shelf life. Use a vinegar-based brine and store in sterilized jars.
Here’s a summary of preservation techniques:
| Technique | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | 6-12 months | Store in airtight containers |
| Freezing | 4-6 months | Blanch before freezing |
| Pickling | 6-12 months | Use sterilized jars |
By following these storage and preservation methods, your mushrooms will stay fresh and delicious. Enjoy your harvest for longer!
Troubleshooting Common Issues
The mushroom fruiting process can sometimes encounter issues. Knowing how to troubleshoot is key. Below, we explore common problems and how to fix them.
Contamination
Contamination is a big problem in mushroom cultivation. It can spoil the whole crop.
- Common Signs: Strange colors, bad smells, and mold growth.
- Prevention Tips:
- Use clean tools and materials.
- Work in a sterile environment.
- Ensure proper air circulation.
- Action Steps:
- Identify the type of contamination.
- Remove contaminated sections immediately.
- Adjust growing conditions.
Slow Growth
Slow growth can frustrate growers. Understanding the reasons helps in quick resolution.
| Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
| Low Temperature | Increase temperature to optimal range. |
| Poor Air Circulation | Ensure proper ventilation. |
| Insufficient Light | Provide adequate light exposure. |
| Incorrect Humidity | Maintain ideal humidity levels. |
Fixing these issues ensures a successful mushroom fruiting process. Happy growing!
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Trigger Mushroom Fruiting?
To trigger mushroom fruiting, maintain high humidity, provide fresh air, and ensure proper lighting. Lower the temperature slightly. Keep the environment clean and free from contaminants.
What Are The Stages Of Mushroom Production?
Mushroom production involves these stages: composting, spawning, casing, pinning, and harvesting. Each stage is crucial for growth.
How Do You Know When Mushroom Blocks Are Ready To Fruit?
Mushroom blocks are ready to fruit when they fully colonize with white mycelium and begin to form small pins.
How Are Mushroom Fruiting Bodies Formed?
Mushroom fruiting bodies form from mycelium under suitable conditions. They emerge when nutrients, humidity, and temperature are optimal.
What Is The Mushroom Fruiting Process?
The mushroom fruiting process involves the development of mature mushrooms from mycelium under optimal conditions.
Conclusion
Mastering the mushroom fruiting process can lead to bountiful harvests. By following these steps, you ensure healthy growth. Remember, patience and consistency are key.
Cultivating mushrooms at home can be both rewarding and educational. Start your mushroom journey today and enjoy fresh, home-grown produce.
Happy growing!
